Shareholders equity is one of the most important ideas in business and finance. It tells you how much value belongs to the owners of a company. If you own shares in a business, this number shows what part of the company is truly yours. Many beginners feel confused when they see this term on a balance sheet. The good news is that it is much simpler than it sounds.
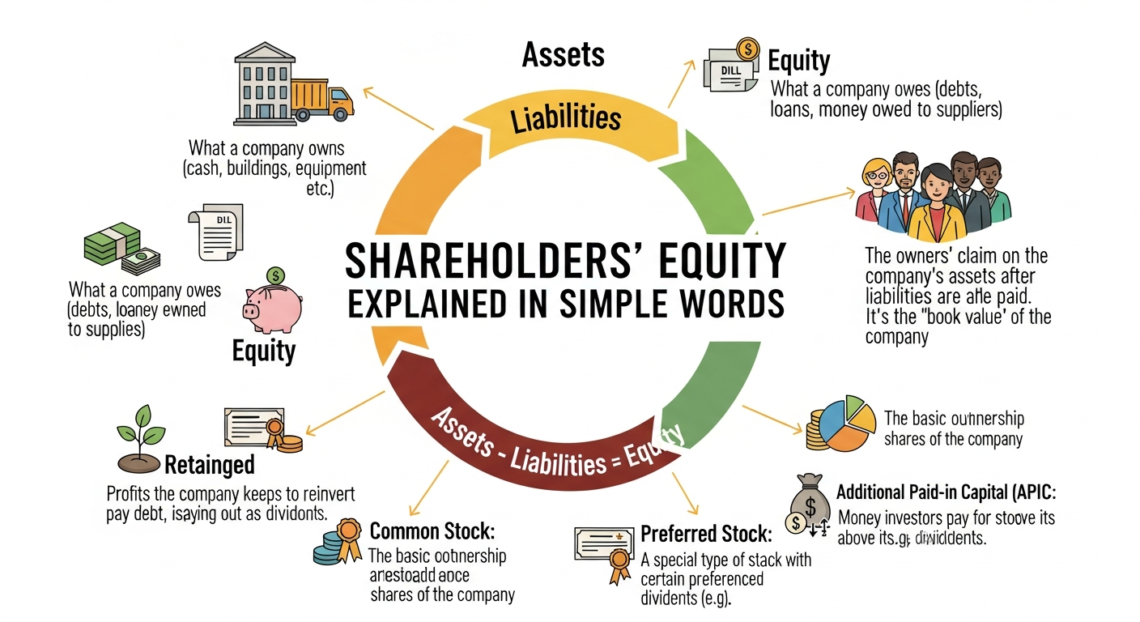
At its core, shareholders equity means what remains after subtracting total liabilities from total assets. In simple words, it answers one question. If a company sold everything and paid all debts, how much money would be left for shareholders? This value helps investors judge a company’s strength, stability, and long-term growth. Understanding shareholders equity also helps students, small business owners, and new investors make smarter financial decisions with confidence.
What Is Shareholders Equity? (Simple Definition)
Shareholders equity represents the ownership value in a company. It belongs to the shareholders, not lenders or creditors. You can think of it as the company’s net worth. When assets are higher than liabilities, shareholders equity is positive. When debts are higher, it becomes negative.
This concept appears on the balance sheet of every company. It shows how much money owners have invested and how much profit the company has kept over time. Shareholders equity includes common stock, retained earnings, and additional paid-in capital. It changes as profits grow, losses occur, or dividends are paid.
For long-term investors, shareholders equity gives a clear picture of financial health. A strong and growing equity balance usually means good management and steady performance. While it should never be viewed alone, it plays a major role in understanding company value.
Shareholders Equity Formula Explained
The formula for shareholders equity is very easy to remember:
Shareholders Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
Assets include cash, inventory, buildings, equipment, and investments. Liabilities include loans, bills, taxes, and other debts. What remains after subtracting liabilities belongs to the shareholders.
This formula works for all businesses, large or small. It helps investors compare companies in the same industry. A company with higher shareholders equity usually has a stronger financial base. However, fast-growing firms may show lower equity at first due to heavy investment. That is why equity should be viewed with other financial data for better judgment.
Why Shareholders Equity Is Important for Investors
Investors use shareholders equity to judge safety and growth potential. It shows how much protection exists if a company faces trouble. Higher equity often means lower risk for investors. It also helps calculate key ratios like return on equity.
Banks and lenders also look at shareholders equity before approving loans. Strong equity signals financial discipline and stability. For long-term investors, rising shareholders equity usually reflects smart reinvestment of profits and healthy business growth.
Understanding this number helps investors avoid weak companies and choose businesses with strong foundations.
Components of Shareholders Equity
Shareholders equity is made up of several important parts. Each tells a different story about the company.
Common stock shows the money raised from issuing shares. Retained earnings reflect profits kept inside the business. Additional paid-in capital shows extra money investors paid above share value. Treasury stock reduces equity when shares are bought back.
Together, these elements explain how ownership value is built over time. A balanced mix of strong retained earnings and stable stock value usually signals a healthy company.
Shareholders Equity vs Owner’s Equity
Many people confuse shareholders equity with owner’s equity. The idea is the same, but the usage is different. Shareholders equity is used for corporations with shareholders. Owner’s equity is used for small businesses or sole proprietors.
Both represent assets minus liabilities. Both show ownership value. The main difference is structure, not meaning. Learning this helps beginners read financial statements without confusion.
How Shareholders Equity Appears on the Balance Sheet
On a balance sheet, shareholders equity appears below assets and liabilities. It balances the accounting equation. This layout helps readers quickly understand financial structure.
Companies report equity changes every period. Profits increase it. Losses reduce it. Dividends lower retained earnings. Watching these changes over time reveals growth trends and management quality.
Positive vs Negative Shareholders Equity
Positive shareholders equity means assets are greater than liabilities. This is usually a good sign. It shows the company owns more than it owes.
Negative shareholders equity means debts exceed assets. This can signal financial trouble. However, some growing companies show temporary negative equity due to heavy expansion. Context always matters.
Real-World Example of Shareholders Equity
Imagine a company owns assets worth $500,000. It has liabilities of $300,000. The shareholders equity equals $200,000. That amount belongs to shareholders.
If profits rise, equity grows. If losses happen, equity shrinks. This simple example helps beginners understand real financial impact.
Shareholders Equity and Business Growth
Strong shareholders equity supports expansion. It allows companies to invest without heavy borrowing. Businesses with rising equity can fund new projects more safely.
Over time, consistent equity growth builds investor trust and market value. It also improves credit strength and financial flexibility.
Common Mistakes When Analyzing Shareholders Equity
Many beginners think high equity always means success. That is not always true. Equity must be compared with profits and cash flow. Others ignore industry differences, which can mislead decisions.
Smart analysis looks at trends, not one number.
How Shareholders Equity Helps Beginners
This concept helps students and new investors understand ownership. It builds confidence when reading reports. It also supports smarter investing decisions.
Learning shareholders equity early creates strong financial habits.
FAQs About Shareholders Equity
What does shareholders equity tell you?
It shows how much value belongs to shareholders after debts are paid.
Is shareholders equity the same as profit?
No. Profit affects equity, but they are different numbers.
Can shareholders equity be negative?
Yes. It happens when liabilities exceed assets.
Why do investors track shareholders equity?
It helps judge financial strength and long-term safety.
Is higher shareholders equity always better?
Usually yes, but it must be compared with profits and growth.
How often does shareholders equity change?
It changes every reporting period based on profits and losses.
Conclusion: Why You Should Understand Shareholders Equity
Shareholders equity is a powerful financial concept that anyone can understand. It shows ownership value, financial strength, and business stability. Whether you are a student, investor, or business owner, learning this concept builds confidence and smarter decision-making.
By understanding shareholders equity, you gain clarity about how companies grow, manage debt, and reward investors. Keep learning, compare trends, and always look beyond a single number. Knowledge like this turns beginners into informed decision-makers.